MBR process (MBR), also known as membrane bioreactor, is a new and efficient wastewater treatment process that combines membrane technology with sewage biological treatment technology. Originated in the United States in the 1970s.
In the field of sewage treatment and water reuse, MBR, also known as Membrane Bio-Reactor, is a new type of water treatment technology that combines activated sludge process with membrane separation technology. There are many types of membranes, which are classified according to the separation mechanism, including reaction membranes, ion exchange membranes, permeable membranes, etc.; according to the nature of membranes, there are natural membranes (biofilms) and synthetic membranes (organic membranes and inorganic membranes); The structural type is classified into a flat type, a tube type, a spiral type, and a hollow fiber type.

The split membrane-bioreactor separates the membrane module from the bioreactor as shown in Figure 3. The mixed liquid in the bioreactor is pressurized by the circulation pump and hits the filter end of the membrane module. Under the pressure, the liquid in the mixed liquid permeates the membrane, and the system processes the water; the solid matter, the macromolecular substance, etc. are trapped by the membrane. The concentrate is returned to the bioreactor. The split membrane-bioreactor is characterized by stable and reliable operation, easy membrane cleaning, replacement and addition; and the membrane flux is generally large. However, under normal conditions, in order to reduce the deposition of pollutants on the surface of the membrane and prolong the cleaning cycle of the membrane, it is necessary to use a circulating pump to provide a higher flow velocity of the membrane surface, a large circulation of water, a high power cost (Yamamoto, 1989), and a pump. The shear forces generated by high-speed rotation can cause inactivation of certain microbial cells (Brockmann and Seyfried, 1997).
The integrated membrane-bioreactor puts the membrane module inside the bioreactor and enters the membrane into the membrane-bioreactor. Most of the pollutants are removed by the activated sludge in the mixture, and then the membrane is pressed by external pressure. Filter out the water. This type of membrane-bioreactor has received a special attention in the field of water treatment in recent years due to the elimination of the mixed liquor circulation system and the relatively low energy consumption by pumping out water; However, the membrane flux is generally relatively low, and membrane fouling is likely to occur, and it is not easy to clean and replace after membrane fouling.
The composite membrane-bioreactor is also a one-piece membrane-bioreactor in the form, except that a filler is added to the bioreactor to form a composite membrane-bioreactor, which changes some of the reactor. Traits.

(1) The removal rate of pollutants is high, the ability to resist sludge expansion is strong, the effluent water quality is stable, there is no suspended matter in the effluent, and bacteria and viruses can be removed, which is a process that does not need to be disinfected after raw water treatment;
(2) Easy to integrate, easy to control automatically, easy to operate, and achieve complete separation of SRT and HRT;
(3) The mechanical interception of the membrane avoids the loss of microorganisms, and the sludge concentration in the bioreactor can reach 35g/L, increasing the volume load and occupying the equipment;
(4) SPR prolongation is beneficial to the slow-proliferation of bacteria, such as the interception and growth of nitrifying bacteria, thereby improving the nitrification capacity of the system and increasing the degradation rate of refractory organic matter;
(5) The amount of excess sludge generated is small, and the sludge disposal cost is low;
(6) Influenced by the surface shearing force of the membrane surface, the average size of the sludge floc is small, and the oxygen transport rate of the sludge is increased, reaching 26% to 60%;
(7) The manufacturing cost is high, the film is easy to be polluted, and the energy consumption is high.
(8) The water quality is clear and translucent;
(9) The effluent water quality is high quality and stable, and the organic pollutants in the effluent water quality are low in CODCr, BOD5, NH3-N, phosphate and SS, and bacteria, viruses and parasite eggs are all separated;
(10) The treatment process is short, the land occupation is small, the secondary settling tank and the filter are omitted, and the investment in engineering is saved;
(11) It can trap all microorganisms in the MBR bioreactor, the sludge concentration is high, the sludge age is long, the nitrification effect is improved, and nitrogen and phosphorus can be effectively removed;
(12) The excess sludge production is small, the oxygen transmission efficiency is up to 60%, and the energy consumption is reduced;
(13) Impact-resistant load, due to the high sludge concentration in the MBR bioreactor, the removal effect of the system is small and the treated effluent is stable when the load changes greatly;
(14) MBR bioreactor is an efficient combination of membrane and biological treatment. The system is compact and simple, stable and flexible in operation, simple in operation management and maintenance, and can realize automatic control.
(15) Small footprint, not subject to installation restrictions
(16) Removal of ammonia nitrogen and refractory organics
(17) Easy operation and management, easy to implement automatic control
(18) Easy to transform from traditional processes
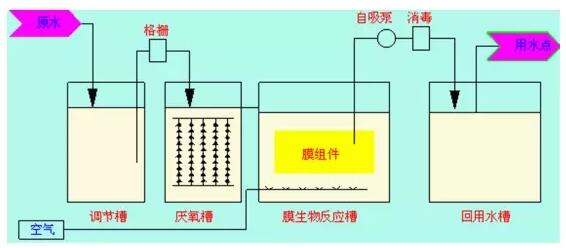
I. Urban sewage treatment and water reuse in buildings
The first wastewater treatment plant using the MBR process in 1967 was built by Dorr-Oliver, USA, which treats 14 m 3 /d of wastewater. In 1977, a wastewater reuse system was put into practical use in a high-rise building in Japan. In 1980, two MBR treatment plants with processing capacities of 10m 3 /d and 50m 3 /d were built in Japan. In the early 1990s, there were 39 such plants operating in Japan with a maximum processing capacity of 500 m 3 /d, and more than 100 high-rise buildings using MBR to treat sewage and return it to the sewer. In 1997, Wessex in the UK established the world's largest MBR system in Porlock, England, with a daily throughput of 2,000 m3. In 1999, it built a 13,000 m3/d MBR plant in Swanage, Dorset.[14] .
In May 1998, the integrated membrane-bioreactor pilot system conducted by Tsinghua University passed the national appraisal. At the beginning of 2000, Tsinghua University built a practical MBR system in Beijing Haidian Township Hospital to treat hospital wastewater. The project was completed and put into use in June 2000 and is now operating normally. In September 2000, Professor Yang Zuoyan from Tianjin University and his research team set up an MBR demonstration project in the Puchen Building of Tianjin New Technology Industrial Park. The system treats 25 tons of sewage per day, and all the treated sewage is used in the bathroom. Flushing and greening, covering an area of ​​10 square meters, the energy consumption per ton of sewage is 0.7kW · h.
Second, industrial wastewater treatment
Since the 1990s, the treatment targets of MBR have been continuously expanded. In addition to the reuse of recycled water and the treatment of fecal sewage, the application of MBR in industrial wastewater treatment has also received extensive attention, such as treatment of food industry wastewater, aquatic product processing wastewater, aquaculture wastewater, cosmetics. Production wastewater, dye wastewater, and petrochemical wastewater have all achieved good treatment results. In the early 1990s, the United States built an MBR system for the treatment of industrial wastewater from an automobile manufacturing plant in Ohio with a treatment scale of 151 m 3 /d. The organic load of the system was 6.3 kg COD/m 3 · d , and the COD removal rate was 94%, most of the oil and grease are degraded. In the Netherlands, a fat extraction processing plant uses traditional oxidation ditch sewage treatment technology to treat its production wastewater. As the scale of production increases, the sludge expands and the sludge is difficult to separate. Finally, the membrane module of Zenon is used instead of the sedimentation tank. good.
Third, micro-polluted drinking water purification
With the wide application of nitrogen fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture, drinking water is also polluted to varying degrees. In the mid-1990s, LyonnaisedesEaux developed the MBR process with both biological nitrogen removal, adsorption of pesticides and turbidity removal. In 1995, the company built a 400m 3 plant with a daily drinking water supply in Douchy, France. The effluent nitrogen concentration is less than 0.1 mg NO 2 /L, and the pesticide concentration is less than 0.02 μg/L.
4. Manure sewage treatment
The organic matter content in the fecal sewage is very high. The traditional denitrification treatment method requires a high sludge concentration, and the solid-liquid separation is unstable, which affects the tertiary treatment effect. The emergence of MBR has solved this problem well and made it possible to treat fecal sewage directly without dilution.
Japan has developed a urine treatment technology called the NS system, and the core part is a system in which a flat membrane device is combined with an aerobic high-concentration activated sludge bioreactor. The NS system was built in 1985 in Koshigaya, Saitama Prefecture, Japan, with a production scale of 10kL/d. In 1989, a new urinary treatment facility was built in Nagasaki Prefecture and Kumamoto Prefecture. The flat membranes in the NS system are installed in a group of about 0.4 m 2 in a group of several dozens, which are arranged in a frame device that can be automatically opened and can be automatically flushed. The membrane material is a polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut off of 20,000. The sludge concentration in the reactor was maintained in the range of 15,000 to 18000 mg/L. By 1994, more than 1,200 MBR systems had been used in Japan to treat more than 40 million people of faecal sewage.
5. Landfill / compost leachate treatment
Landfill/compost leachate contains high concentrations of pollutants, and its water quality and quantity vary with climatic conditions and operating conditions. MBR technology was used by many sewage treatment plants before 1994 to treat this type of sewage. The combination of MBR and RO technology not only removes SS, organic matter and nitrogen, but also effectively removes salts and heavy metals. Recently, Envirogen Corporation of the United States developed an MBR for landfill leachate treatment and built a facility with a daily capacity of 400,000 gallons (about 1500 m 3 /d) in New Jersey, which was put into operation at the end of 2000. The MBR uses a naturally occurring mixed bacteria to decompose hydrocarbons and chlorinated compounds in the leachate, which are treated to a concentration of 50 to 100 times that of conventional wastewater treatment plants. The reason for this treatment is that MBR is able to retain high-efficiency bacteria and achieve a bacterial concentration of 50,000 mg/L. In the on-site pilot test, the COD of the feed liquid is several hundred to 4,000, and the removal rate of pollutants is over 90%.
CCTV Tool, Network Installation Tool, CCTV Installation Tool, Stripping Tool, Crimping Tool
Chinasky Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.cctv-products.com