RFID (Radio Frequency IDenTIficaTIon) radio frequency identification technology, also known as electronic tag, radio frequency identification, is a communication technology. Compared with the traditional magnetic card and IC card technology, it has the characteristics of non-contact, fast reading speed and no wear, and has been rapidly developed in recent years. In order to strengthen the understanding of Chinese engineers on this technology, this paper introduces in detail the working principle, classification, standards and related applications of RFID technology. 
RFID technology uses wireless radio frequency to perform non-contact two-way data transmission between the reader and the RF card to achieve the purpose of target recognition and data exchange. Compared with traditional bar code, magnetic card and IC card, RF card has non-contact, fast reading speed, no wear, no environmental impact, long life, easy to use and anti-collision function. It can process multiple sheets at the same time. card. In foreign countries, radio frequency identification technology has been widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, transportation control management.
Rfid system composition and working principle The most basic RFID system consists of three parts:
1. Tag (RF card): It consists of a coupling component and a chip. The tag contains a built-in antenna for communication with the RF antenna.
2. Reader: A device that reads (and can also write in the card) the tag information.
3. Antenna: Pass RF signals between the tag and the reader.
Some systems also connect to an external computer (host computer system) through the RS232 or RS485 interface of the reader for data exchange. 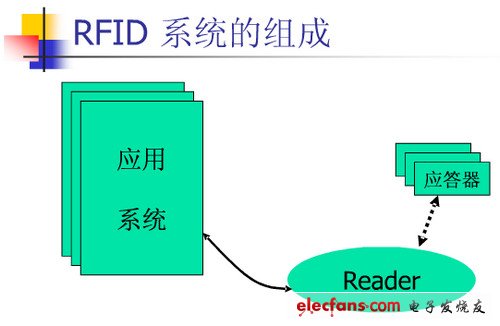
The basic working process of the system is: the reader transmits a certain frequency of the radio frequency signal through the transmitting antenna, and when the radio frequency card enters the working area of ​​the transmitting antenna, an induced current is generated, and the energy obtained by the radio frequency card is activated; the radio frequency card transmits the information such as its own code through the card. The antenna is sent out; the receiving antenna of the system receives the carrier signal sent from the RF card, and transmits it to the reader through the antenna adjuster, and the reader demodulates and decodes the received signal and sends it to the background main system for related processing; the main system According to the logic operation, the legality of the card is judged, corresponding processing and control are performed for different settings, and a command signal is issued to control the action of the actuator.
Different in coupling mode (inductor-electromagnetic), communication flow (FDX, HDX, SEQ), data transmission method from RF card to reader (load modulation, backscatter, higher harmonics) and frequency range The contactless transmission method is fundamentally different, but all readers are similar in terms of functional principle and thus the design and construction. All readers can be simplified into two basic modules: high frequency interface and control unit. The high frequency interface includes a transmitter and a receiver, the functions of which include: generating high frequency transmit power to activate the radio frequency card and providing energy; modulating the transmit signal for transmitting data to the radio frequency card; receiving and demodulating the radio frequency card from the radio frequency card High frequency signal. The high-frequency interface design of different radio frequency identification systems has some differences, and the high-frequency interface schematic diagram of the inductive coupling system is shown in the figure. 
The functions of the reader's control unit include: communicating with the application system software and executing commands from the application system software; controlling the communication process with the RF card (master-slave principle); encoding and decoding of the signals. For some special systems, there are also anti-collision algorithms, encryption and decryption of data to be transmitted between the RF card and the reader, and additional functions such as authentication between the RF card and the reader.
The read/write distance of the RFID system is a key parameter. Currently, long-distance radio frequency identification systems are expensive, so it is important to find ways to increase their read and write distances. Factors affecting the reading and writing distance of the RF card include the antenna operating frequency, the reader's RF output power, the reader's receiving sensitivity, the power consumption of the RF card, the Q value of the antenna and the resonant circuit, the antenna direction, the coupling of the reader and the RF card. Degree, as well as the energy obtained by the RF card itself and the energy of the transmitted information. The reading distance and writing distance of most systems are different, and the writing distance is about 40% to 80% of the reading distance. 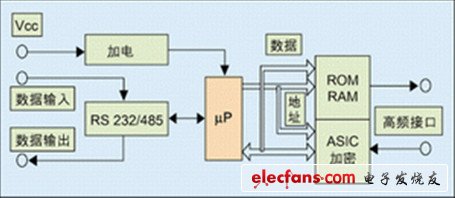
Standards and classifications of rfid RF cards Many companies currently producing RFID products use their own standards, and there is no uniform standard in the world. Currently, several standards for RF card use are ISO10536, ISO14443, ISO15693, and ISO18OOO. The most widely used are ISO14443 and ISO15693, both of which consist of physical characteristics, RF power and signal interface, initialization and anti-collision, and transmission protocol.
According to different ways, RF cards have the following classifications:
1. Divided into active card and passive card according to the power supply mode. Active means that there is a battery in the card to provide power, which has a long working distance, but has a limited life, large volume, high cost, and is not suitable for working in a harsh environment; there is no battery in the passive card, it uses beam power supply technology The received RF energy is converted into a DC power supply to supply power to the card circuit, and its working distance is shorter than that of the active card, but the service life is long and the working environment is not high.
2. According to the carrier frequency, it is divided into low frequency radio frequency card, intermediate frequency radio frequency card and high frequency radio frequency card. The low-frequency RF card mainly has two kinds of 125 kHz and 134.2 kHz. The frequency of the intermediate frequency RF card is mainly 13.56 MHz, and the high frequency RF card is mainly 433 MHz, 915 MHz, 2.45 GHz, 5.8 GHz, and the like. Low-frequency systems are mainly used in short-range, low-cost applications such as most access control, campus cards, animal regulation, and cargo tracking. The IF system is used for access control and application systems that need to transmit large amounts of data; the high frequency system is used in applications where long read/write distance and high read/write speed are required, and the antenna beam direction is narrow and the price is high. Application in systems such as highway tolls.
3. According to the different modulation methods, it can be divided into active and passive. The active RF card actively sends data to the reader with its own RF energy; the passive RF card uses modulated scatter to transmit data. It must use the carrier of the reader to modulate its own signal. This type of technology is suitable for use in access control or In traffic applications, the reader can ensure that only a range of RF cards are activated. In the case of obstacles, with the modulation scattering method, the energy of the reader must come and go through the obstacle twice. The signal transmitted by the active RF card only passes through the obstacle once, so the active RF card is mainly used in the application of obstacles, the distance is longer (up to 30 meters).
4. According to the working distance, it can be divided into close-coupled card (acting distance less than 1 cm), near-coupled card (acting distance less than 15 cm), loose coupling card (acting distance is about 1 m) and long-distance card (acting distance from 1 m) To 10 meters, or even further).
5. According to the chip, it is divided into read-only card, read-write card and CPU card.
Multifunctional rechargeable vacuum cleaners: With high power and high cleaning efficiency, this multifunctional Handheld Vacuum Cleaner can be used for cleaning hidden dirty of notebook keyboard, printer, pet food, office, kitchen table, or other small household appliances. And the portable wireless vacuum cleaner can be used for cleaning car vent, dashboard, storage cabinet, sand, dust, paper, food debris, and so on too.
As a mini Portable Vacuum Cleaner, it is very
convenient for storage. With blow and suction function, the cordless vacuum
cleaner makes the cleaning much easier. The battery capacity is 2000Mah and you
can use it for cleaning 20 minutes every time. As a Rechargeable Vacuum Cleaner, it can be recharged by connecting it to a source of direct current or a computer. It is very easy and convenient to use.
Multifunctional Rechargeable Vacuum Cleaner
Rechargeable Vacuum,Multifunction Cleaner Vacuum Cleaner,Multi Function Vacuum Cleaner,Multifunction Carpet Cleaner
SHENZHEN HONK ELECTRONIC CO., LTD , https://www.honktech.com