Luo Wen, Dean of China Electronic Information Industry Development Institute
Introduction: The German Industry 4.0 strategy has presented us with a brand new industrial blueprint, an in-depth analysis of its vision and key points, and insight into the purpose and strategic intent of Germany's proposed Industry 4.0. Under the new background of development, we will closely integrate the characteristics of the age of informatization with the historical process of industrialization in our country. We will use the deep integration of the two industries as the main line to inject new impetus into the promotion of industrial transformation and upgrading, so as to occupy the process of industrialization. This is an important opportunity for China's 4.0 strategy to promote industrial restructuring and upgrading in China.

The concept of “Industry 4.0†originated from the 2011 Hannover Industrial Fair in Germany. Its original intention was to improve German manufacturing through the application of new technologies such as the Internet of Things. Driven by the academic and industrial sectors such as the German Academy of Engineering, the Fraunhofer Association, and Siemens, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology incorporated the “Industry 4.0†project into the “High-tech Strategy 2020†in 2013. Among the top ten future projects, it plans to invest 200 million Euros to support the development and innovation of a new generation of revolutionary technologies in the industrial field. Subsequently, the German Machinery and Manufacturers Association (VDMA) established the "Industry 4.0 Platform", and the German Institute of Electrical, Electronics and Information Technology published the first industrial 4.0 standardization roadmap in Germany.
The German government believes that although Germany has a strong machinery and equipment manufacturing industry, China poses a competitive threat to German industry, and the United States has also adopted various plans to promote the development of advanced manufacturing. Therefore, the purpose of formulating the “Industry 4.0†strategy is to "Ensure the future of German manufacturing." At present, it is at a critical time when China vigorously promotes the deep integration of the two industries and promotes industrial transformation and upgrading. Germany's implementation of the concept, content, and practices of the “Industry 4.0†strategy deserves our serious attention, learning, and positive responses.
"Industry 4.0" Strategic Vision and Key Points
Different from the popular third industrial revolution in the United States, Germany describes the progressive progress in manufacturing technology as the four stages of the industrial revolution, namely the evolution of Industry 4.0 (Figure 1).
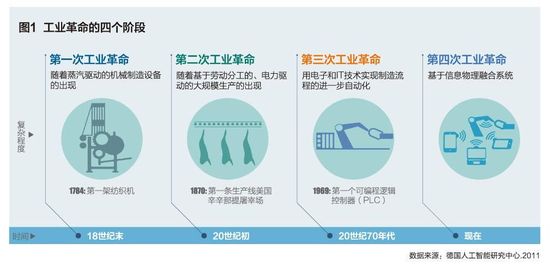
Industry 1.0 . From the 1960s to the mid-19th century, factory mechanization through hydraulic and steam engines was called Industry 1.0. The result of this industrial revolution was that mechanical production replaced manual labor, and the economic society transformed from agriculture and handicraft industries to the model of industrial development and mechanical manufacturing that promoted economic development.
Industry 2.0 . From the latter half of the 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century, the large-scale production of electric drive products based on the division of labor can be called Industry 2.0. This industrial revolution, through the successful separation of parts production and product assembly, created a new model for mass production of products.
Industry 3.0 . Beginning in the 1970s and continuing until now, the widespread use of electronics and information technology has led to the continuous automation of the manufacturing process, which can be referred to as Industry 3.0. Since then, the machine has been able to gradually replace human operations, not only took over a considerable proportion of "manual labor" but also took over some "brain labor."
Industry 4.0 . German academia and industry believe that in the next 10 years, intelligence based on the Cyber-Physical System (CPS) will enable humans to step into the fourth industrial revolution led by intelligent manufacturing. The digitalization of the product life cycle and the entire manufacturing process and the integration of modules based on information and communication technology will form a highly flexible, personalized and digital product and service production model.
“Industry 4.0†has shown us a brand new industrial blueprint: In an “intelligent, networked worldâ€, the Internet of Things and the Internet of Things (Service Internet Technology) will penetrate into all key areas and create new value. It will gradually change, the industrial chain division of labor will be reorganized, the traditional industry boundaries will disappear, and various new fields of activity and forms of cooperation will emerge.
First, Industry 4.0 will make the industrial production process more flexible and strong. This will enable the dynamic, timely optimization and self-organizing value chain to become a reality and bring about the optimization of different criteria such as cost, availability and resource consumption. Including all the factors and resources in the manufacturing field to form a new circular network, the unique identifiability of smart products, personalized product customization, and a highly flexible work environment.
Second, Industry 4.0 will develop new business models and cooperation models. These models will strive to ensure that potential commercial profits are shared fairly among all stakeholders throughout the value chain, including those newly entered stakeholders. At the same time, features such as Industry 4.0 "Networked Manufacturing," "Self-organized and adaptable logistics," and "Integrated Customer Manufacturing Engineering" have also led it to pursue new business models to take the lead in meeting dynamic business networks rather than individual companies. This will lead to a series of issues such as financing, development, reliability, risk, liability and intellectual property, and technical security.
Again, Industry 4.0 will bring about entirely new changes in working methods and environments. The new collaborative way of working enables the work to be carried out from the factory and carried out in a virtual and mobile manner. Employees will have a high degree of management autonomy and can more actively invest in and regulate their work. At the same time, with the dramatic changes in the working environment and working methods, the employment ratio of the elderly and women can be greatly increased, ensuring that changes in the demographic structure will not affect the current standard of living.
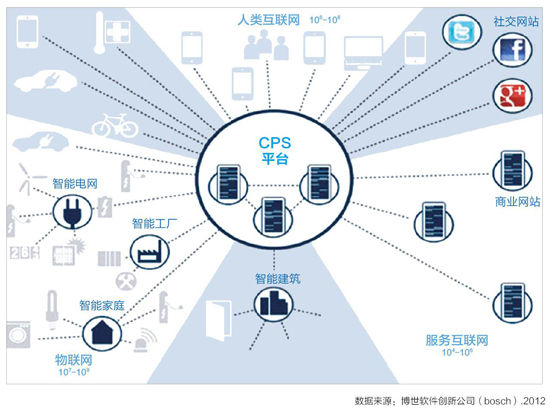
Finally, Industry 4.0 will promote the formation of a new platform for information physics systems. The new information physics system platform can be connected to all participating personnel, objects and systems. It will provide comprehensive, fast, safe and reliable service and application business processes to support collaborative manufacturing, service, analysis and prediction in mobile terminal equipment and business networks. Process, etc., as shown in Figure 2.
The main points of the German "Industry 4.0" strategy can be summarized as follows: building a network, studying two major themes, implementing three integrations, and implementing eight plans.
Build a network: network of information physics systems. The information physics system is the connection of physical devices to the Internet, allowing the physical devices to have five functions of computing, communication, precise control, remote coordination, and autonomy, thereby realizing the convergence of the virtual network world and the real world. CPS can closely link resources, information, objects and people to create Internet of Things and related services, and transform production plants into a smart environment. This is the basis for achieving Industry 4.0.
Research two major themes: smart factory and smart production. The "smart factory" is a key component of the future intelligent infrastructure, focusing on the research of intelligent production systems and processes and the realization of networked distributed production facilities. The focus of “smart production†is to apply advanced technologies such as human-computer interaction, intelligent logistics management, and 3D printing to the entire industrial production process, thereby forming a highly flexible, personalized, and networked industrial chain. Intelligent production process is the key to achieving Industry 4.0.
Implement three integrations: horizontal integration, vertical integration, and end-to-end integration. "Industry 4.0" will use ubiquitous sensors, embedded terminal systems, intelligent control systems, and communication facilities to form an intelligent network through CPS, enabling people, people and machines, machines and machines, and services and services to be interconnected. This enables horizontal, vertical and end-to-end integration. “Horizontal integration†is a kind of resource integration achieved between enterprises through the value chain and information network. It is to achieve seamless cooperation between enterprises and provide real-time products and services; “vertical integration†is based on the network in the future of smart factories. The manufacturing system realizes customized production and replaces traditional fixed production processes (such as production lines); “end-to-end integration†refers to the digital integration of engineering throughout the entire value chain and is based on the premise of digitalization of all terminals. An integration based on the value chain and different companies is achieved, which will maximize personalization.
Implementation of the eight plans: The basic guarantee for the realization of "Industry 4.0". The first is the standardization and reference architecture. There is a need to develop a single set of common standards. Network connectivity and integration between different companies will be possible. The second is to manage complex systems. Proper planning and explanatory models can provide the basis for managing increasingly complex products and manufacturing systems. The third is a comprehensive set of industrial broadband infrastructure. A reliable, comprehensive, high-quality communication network is a key requirement of "Industry 4.0". The fourth is safety and security. While ensuring that production facilities and products themselves cannot pose a threat to people and the environment, they must prevent the abuse of production facilities and products and unauthorized access. Fifth, the organization and design of the work. With the change of work content, process and environment, new requirements have been put forward for management work. Sixth, training and continuous professional development. It is necessary to help workers cope with new demands from work and skills by establishing lifelong learning and continuing career development plans. Seven is the regulatory framework. New issues such as corporate data, responsibilities, personal data, and trade restrictions brought about by innovation need to be supervised by appropriate means including guidelines, model contracts, agreements, and audits. Eighth, resource utilization efficiency. Need to consider and weigh the large amount of raw materials and energy consumption to bring many risks to the environment and safe supply.
In general, the core of the “Industry 4.0†strategy is to realize real-time connectivity, mutual recognition, and effective communication of people, equipment, and products through CPS networks, so as to build a highly flexible, personalized and digital smart manufacturing model. Under this model, production shifts from centralized to decentralized, and scale effect is no longer a key factor in industrial production; products shift from convergence to individuality, and future products will be produced entirely in accordance with individual wishes, and in extreme cases will become automated, Individualized single-piece manufacturing; Users transition from part-participation to full-scale participation. Users not only appear at both ends of the production process, but also participate in the entire process of production and value creation in a wide range and in real time.
"Industry 4.0" Strategic Purpose and Intent
Actively respond to the revolution in the new technology industry and compete for the right to discourse in the international industry. Developed countries such as the United States have revitalized the manufacturing industry as their top priority in recent years. At present, breakthroughs in the areas of information and communication, new energy, new materials, and biology are nurturing and catalyzing a new round of technological and industrial changes. In order to win the initiative in the international competition, the United States began to adjust its economic development strategy in early 2009. In December of the same year, it announced the “Rejuvenation of the US Manufacturing Frameworkâ€; in June 2011 and February 2012, it launched the Advanced Manufacturing Partner Program and The "Advanced Manufacturing Country Strategic Plan" and through active industrial policies encourage manufacturing companies to return to the United States. From a practical point of view, the share of the U.S. manufacturing industry in GDP rose from 12% in 2010 to 15% in 2013. In addition, Japan, South Korea, etc. also pay special attention to the support of new industries represented by information technology and new energy. For example, in March 2009, Japan introduced an information technology development plan to promote the application of IT technology in medical and administrative fields. In April of the same year, it launched a new growth strategy to support the development of industries such as environmentally friendly vehicles, electric vehicles, and solar power. South Korea has formulated the “New Growth Power Planning and Development Strategy†and identified a total of 17 emerging industries in the fields of green technologies and cutting-edge industries as new growth drivers.
Emerging economies such as China have rapidly increased their influence and competitiveness in the global manufacturing industry. From 1990 to 2011, the added value of manufacturing in traditional industrialized countries increased by an average of 17%, while the emerging industrial countries represented by the BRIC countries (China, Russia, India, and Brazil) increased by 179%. In emerging economies, China's manufacturing output accounts for about 20% of the world's total, making it the world's largest manufacturing country. At the same time, the Chinese government has formulated the "Industrial Transformation and Upgrade Plan" and the "National Strategic Emerging Industries Development Plan" to actively promote the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry. In 2011, the Indian Ministry of Communications and Information Technology formally launched the “Innovation Center for Information Physics Systems†to conduct research in various fields including humanoid robots. According to the latest survey by Zebra Tech, even today, Indian companies use the Internet of Things technology at the forefront of the world.
Germany does not need to guide enterprises through strategic adjustment to actively compete for the commanding heights of international manufacturing competition. The development of a new generation of information and communication technologies has spawned innovations and applications such as mobile Internet, big data, cloud computing, and industrial programmable controllers, and has promoted profound changes in manufacturing production methods and development models. In this process, although Germany has world-class machinery and equipment manufacturing, especially in the field of embedded systems and automation engineering, the challenges facing the German industry and its relative weaknesses are also very obvious. On the one hand, the global competition in the field of mechanical equipment is increasingly fierce. Not only does the United States actively revitalize the manufacturing industry, Asian machinery and equipment manufacturers are also catching up and threatening the status of German manufacturers. On the other hand, software and internet technologies are relatively weak industries in Germany. In order to maintain its position as a leading global equipment manufacturing supplier and its advantages in the field of embedded systems, facing the challenge of a new round of technological revolution, Germany has put forward its own “Industry 4.0†strategy with the aim of giving full play to Germany’s traditional advantages and vigorously promoting it. The application of Internet of Things and service Internet technology in the manufacturing industry is preemptive in the process of moving to the fourth stage of industrialization, and competes with the United States and Japan for the right to speak of the new technological industrial revolution.
Conform to the new trend of global manufacturing development and push forward the objective requirements of the new model of intelligent manufacturing. The application of information technology in equipment, management, and trading has continued to deepen, and the promotion of flexible production, intelligent manufacturing, and service-based manufacturing has increasingly become an important direction for the transformation of production methods. The extensive application of information network technology has enabled the rapid popularization of fully automated production lines that integrate production experience, mature technology, and scientific methods. This not only greatly increases production efficiency, but also greatly promotes the seamless integration of production processes and collaborative manufacturing among enterprises. The concept of the Internet has expanded into industrial production and service areas. It has spawned new modes such as crowdsourcing design and personalized customization. It will promote the real-time interaction between producers and consumers, so that products produced by enterprises will no longer converge in large numbers but become more personalized. The wide application of information technology, big data, etc., also continues to promote the production of products from the traditional product manufacturing as the core to provide a rich connotation of products and services until the total solution to provide customers. The boundaries between Internet companies and manufacturing, production, and service companies are increasingly blurred. More and more facts have shown that the development and application of information technology, especially Internet technology, is rapidly advancing the profound changes in manufacturing production methods and development models with unprecedented breadth and depth.
"Industry 4.0" emphasizes that the integration of information networks and physical production systems to change the current industrial production and service model will become an important means for enterprises to increase product added value and enhance market competitiveness. In the “Industry 4.0†era, products and production equipment and different production equipment are connected to each other through data interaction, so that the vertical direction of the factory can be integrated even between the factory and the factory. Smart. In 2013, the German Zeiss Group demonstrated a system called PiWeb at the European Machine Tool Show. The system can realize the network sharing of machine measurement data of multinational companies distributed in factories in different regions, and realize simultaneous monitoring of data from different factories around the world. Companies such as Bosch, Mercedes-Benz and Volkswagen in Germany have already begun to use this system. In addition, at the Hannover Messe 2014, Germany demonstrated the world’s first “Industry 4.0†demonstration system in which 10 companies participated in joint research and development to demonstrate the possibility of this concept. This shows that Germany can not only provide industrial products manufactured using intelligent manufacturing systems to the world, but also strive to become the creator and supplier of advanced intelligent manufacturing technologies, thereby promoting intelligent and service-oriented manufacturing in Germany.
China's Enlightenment of "Industry 4.0" Strategy
The integration of two deepens as the main focus. The "Industry 4.0" strategy of Germany and China's proposed deep integration of the two have many similarities. To a certain extent, the integration of the two can be referred to as the 3.0 of China's industry, and the deep integration of the two can be said to be 4.0 of our country's industry. Under the new background of development, only by combining the characteristics of the era of informatization with the historical process of industrialization in our country and integrating the deep integration of the two industries as the main line, can we inject new impetus into the promotion of industrial transformation and upgrading, and we can also move forward in the process of industrialization. Take the initiative.
Advance deployment and construction of a national information physical system network platform. The information physics system will change the way humans interact with the physical world. The integration of three kinds of resources: material productivity, information productivity, energy, materials, and information will enable the real revolutionary transformation of the industry in the future and have a profound impact on the future world. The world’s industrial powers such as the United States and Germany have all attached great importance to the construction of the information physics space, strengthened the strategic foresight deployment, and made active research progress. To compete for future competition, China must take a step forward in building an information physics system network platform. On the one hand, we will strengthen the overall layout of CPS in the country's new information development strategy, and study and formulate the strategic objectives, key tasks, development paths, and policy measures for CPS construction. At the same time, we will strengthen forward-looking deployment and application promotion in such areas as manufacturing development, smart city construction, national networks, and information security. On the other hand, the United States can learn from the United States to establish a "National Manufacturing Innovation Network Center" approach to set up a number of national information physical system network platform, responsible for undertaking basic theoretical research, organizational strength research and development breakthrough CPS software, sensors, mobile terminal equipment and other tools and equipment Promote the development and application of enterprises in key industries.
Launched a national major national intelligent manufacturing project. Intelligent manufacturing has become a new trend in the development of global manufacturing, and smart devices and production methods will certainly widely replace traditional production methods in the future. At present, China has initially formed a complete industrial system in areas such as intelligent measurement and control, CNC machine tools, robots, new sensors, and 3D printing. However, on the whole, the development of China's manufacturing industry still focuses on the simple expansion of reproduction. The task of transforming and upgrading traditional manufacturing through smart products, technologies, equipment, and ideas is arduous and urgent. It is recommended that the implementation of special projects for smart manufacturing be initiated at the national level, technological breakthroughs should be intensified, application demonstrations carried out, and the transition from manufacturing to intelligent development should be promoted. The first is to break through intelligent robots. Carry out research on core technologies such as system integration, design, manufacturing, testing and testing of intelligent robots and intelligent equipment, and overcome key components such as precision reducers, servo drives, and sensors. The second is to carry out digital factory application demonstration. In the whole country, select the pilot demonstration enterprises by sub-industry, give support, and build a digital manufacturing demonstration plant to play its "seed" role. The third is to promote the application of manufacturing big data. Taking the leading enterprises in the industry as the guide, encourage them to apply big data technology to improve the level of intelligent decision-making and operational efficiency in manufacturing, supply chain management, product marketing and service.
Standards lead the convergence of information network technology and industry. The key to the “Industry 4.0†strategy is to establish a networked society in which people, machines and resources are interconnected. Data exchange, identification, processing, and maintenance of various terminal equipment and application software must be based on a set of standardized systems. In order to ensure the smooth realization of "Industry 4.0", Germany ranks first in eight actions, and at the same time it proposes to set up a working group under the "Industry 4.0" platform to deal specifically with the issues of standardization and reference architecture. In December 2013, the German Institute of Electrical, Electronics and Information Technology published the first "Industry 4.0" standardization roadmap in Germany. It can be said that the standard first is the outstanding feature of the "Industry 4.0" strategy. To this end, in promoting the deep integration of information network technology and industrial enterprises, we should also attach great importance to the role of standardization in the development of the industry, and formulate a standardized road map of "intensified integration between the two industries" to guide the enterprise's advancement. Information construction. At the same time, efforts must be made to achieve the internationalization of standards, so that the standards set by China will be widely adopted internationally in order to seize the commanding heights and discourse power of future industrial competition.
Build an institutional safeguard system that is conducive to industrial transformation and upgrading. The German “Industry 4.0†strategy places great emphasis on the issues of conflict between industrial innovation, organizational innovation and existing systems. On the one hand, “Industry 4.0†increases the complexity of management and control. The formulation of technical standards needs to comply with corresponding laws and regulations. On the other hand, it also needs to formulate corresponding rules and regulations to promote technological innovation. "Industry 4.0" has adopted a series of measures to strengthen institutional guarantees, such as setting up a full-time working group to deal with various issues, formulating and implementing security support actions, and establishing training and re-education systems. In the promotion of industrial transformation and upgrading, our country is also facing issues related to institutional safeguards. Therefore, it is very necessary to establish and improve long-term mechanisms conducive to industrial transformation and upgrading, such as intellectual property protection systems, laws and regulations in key areas such as energy conservation and environmental protection, quality and safety, personnel training and incentive mechanisms, so as to promote the promotion of industrial transformation and upgrading. System protection.
Production, education and research jointly promote the development of manufacturing innovation. The German “Industry 4.0†was jointly initiated by the German Academy of Engineering, the Fraunhofer Association, and Siemens, and the members of the working group were also made up of representatives of production, education and research. Therefore, once the “Industry 4.0†strategy was proposed, it quickly gained positive responses from academics and industry. In fact, the motive of the government to support cooperation between industry, universities, and research institutes is not solely based on market considerations. Promoting competition through cooperation, innovation, production, and research has often become an important strategic intention of developed countries. China should fully absorb and learn from the joint model of production, learning and research in developed countries. On the one hand, for different types of spontaneous industry-university-research cooperation networks or industrial R&D alliances, the government must promote its development through guidance and support; on the other hand, select several Pilot projects in key industries and key technology areas, with leading companies in the industry as the leader, and universities and scientific research institutions with strong scientific research strength, form a variety of research and development alliances for research, production, research and development, and fully mobilize all resources and strengths to jointly advance technology research and development and application. Promotion.
Phase Control Thyristor is the abbreviation of thyristor, also known as silicon controlled rectifier, formerly referred to as thyristor; thyristor is PNPN four-layer semiconductor structure, it has three poles: anode, cathode and control pole; thyristor has silicon rectifier The characteristics of the parts can work under high voltage and high current conditions, and their working processes can be controlled and widely used in electronic circuits such as controlled rectifiers, AC voltage regulators, contactless electronic switches, inverters, and inverters.
Phase Control Thyristor,Ir Phase Control Thyristor,Stud Phase Control Thyristor,Electronic Component Phase Control Thyristor,High Power Phase Control Thyristor
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.pst-thyristor.com