introduction
With the progress of society and the development of technology, multimedia services continue to grow, and people's requirements for network bandwidth also increase. The communication network is developing towards IP and broadband. The communication network is composed of three parts: transmission network, switching network and access network. At present, China's transmission network has basically realized digitization and optical fiber; the exchange network has also realized program control and digitization; and the access network is still connected to the central office through twisted pair, and can only achieve a transmission rate of 56 kb / s. Meet people's urgent needs for multimedia information. Large-scale transformation of the access network to upgrade to FTTC (fiber to the road) or even FTTH (fiber to the home) requires high costs and is difficult to achieve in the short term. XDSL technology realizes the high-speed transmission of data on the telephone line, but most home telephone lines are not many, which limits the number of computers that can connect to the Internet, and it is extremely inconvenient to lay transmission cables in each room. The most cost-effective and convenient basic equipment is the power cord. Using the power cord as a transmission medium, there is no need to construct new lines inside the home, and the cost is low. As a communication channel, the power line requires little or no maintenance, and can be flexibly plug and play. In addition, since there is no need to pay for phone calls, the monthly fee is cheap.
The high-speed data transmission of the power line has made it possible for the power line to be a communication medium. Where power lines are laid, various Internet data can be transmitted through the power lines to realize data communication, connecting to a local area network or accessing the Internet. The transmission of various Internet data through power lines can greatly promote the popularity of the Internet. This technology can also combine home computers and electrical appliances into a network that can communicate with each other to form a new type of intelligent home grid. Users can monitor and manage household appliances through the Internet from anywhere; can directly implement power meter reading and grid automation The functions of remote signaling, telemetry, remote control, and remote adjustment without having to lay additional communication channels. Therefore, it is very necessary to study power line communication.
1 Basic principles of OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division MulTIplexing) is an orthogonal multi-carrier modulation MCM method. In a traditional digital communication system, symbol sequence modulation is serially transmitted on a carrier wave, and the frequency of each symbol can occupy the entire available bandwidth of the channel. OFDM is a parallel data transmission system, which is composed of N sub-carriers at equal intervals in frequency. They separately modulate an independent way of data information, and the signals of N sub-carriers are added and sent at the same time after the modulation. Therefore, the spectrum of each symbol only occupies a part of the entire bandwidth of the channel. In the OFDM system, by selecting the carrier interval, these subcarriers maintain the orthogonal characteristics of the spectrum throughout the symbol period. The signals on each subcarrier overlap each other in the spectrum, and the receiving end uses the orthogonal characteristics between the carriers. Sending information can be restored without distortion, thereby improving the spectrum utilization rate of the system. Figure 1 shows the basic principle of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM. Consider the symbol sequence (do, d1, ..., dn-1) transmitted in a cycle. Each symbol di is a complex signal di = ai + jbi after baseband modulation, and the interval of the serial symbol sequence is △ t = l / fs, Where fs is the symbol transmission rate of the system. After serial-to-parallel conversion, they modulate N sub-carriers (fo, f1, ..., fn-1) respectively. The N sub-carriers are frequency-division multiplexed over the entire channel bandwidth, and the frequency interval between adjacent sub-carriers is 1 / T, the symbol The period T increases from Δt to NΔt. The synthesized transmission signal D (t) can be represented by its low-pass complex envelope D (t).
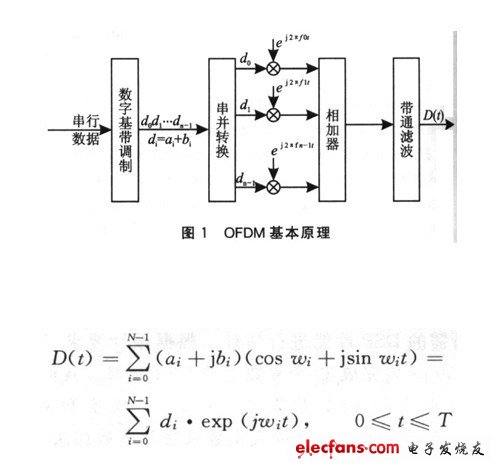
Where ωi = -2π · △ f · i, △ f = 1 / T = 1 / N △ t. In the symbol period [O, T], the transmitted signal is D (t) = Re {D (t) exp (j2πfot)}, 0≤t≤T.
If D (t) is sampled with the symbol transmission rate fs as the sampling rate, there are a total of N sampled values ​​within one cycle. Let t = m △ t, the sampling sequence D (m) can be expressed by the inverse discrete Fourier transform of the symbol sequence (do, d1, ..., dn-1). which is

Therefore, the modulation and demodulation processes of the OFDM system are equivalent to discrete inverse Fourier transform and discrete Fourier transform processing. The core technology is discrete Fourier transform. If digital signal processing (DSP) technology and FFT fast algorithm are used, no beam filter bank is needed, and the implementation is relatively simple.
2 Hardware composition of power line data transmission equipment
The hardware block diagram of the power line data transmission equipment is shown in Figure 2.

2. 1 digital signal processing unit TMS320VC5402
The use of digital signal processing means to achieve MODEM requires extremely high computing power and extremely high computing speed. Before the emergence of high-speed DSP, digital signal processing can only use ordinary microprocessors. Due to the speed limitation, the highest speed of the MODEM achieved is generally 2400b / s. Since the late 1970s, Intel introduced the first-generation DSP chip Intel 2920, and a large number of high-speed DSP chips have emerged in the past 20 years, thereby making it possible to realize the high-speed DSP MCODEM in the voice band.
The TMS320 series is cost-effective and has complete domestic development methods. Since TI's first generation product TMS32010 in the early 1980s, it has been launching TMS32020, TMS320C25, TMS320C30, TMS320C40 and the fifth generation at a rate of a new generation every two years Substitute product TMS320C54X.
According to the signal processing capability required for OFDM modem implementation, this paper chooses TMS320VC5402 as a data pump to complete various algorithms such as FFT, make full use of its software and hardware resources, and realize a cost-effective OFDM high-speed power line data transmission device.
TMS320C54X is a mid-to-high-end 16-bit fixed-point DSP series device launched by TI for communication applications. This series of devices is powerful and flexible. Compared with previous generations of DSP, it has the following outstanding advantages:
◇ Faster speed (40 ~ 100 MIPS);
â—‡ The instruction set is more abundant;
â—‡ More addressing options;
â—‡ Two 40-bit accumulators;
â—‡ Hardware stack pointer;
â—‡ Support block repeat and ring buffer management.
A fan VFD, or variable frequency drive, is a specialized device utilized for controlling and regulating the speed of fan motors. By adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor, the VFD enables precise control over the rotational speed of the fan. This functionality allows for efficient fan operation, improved energy savings, and enhanced performance in applications such as HVAC systems and industrial fans.
The primary benefit of a fan VFD is its ability to achieve energy efficiency. Traditional methods of controlling fan speed, such as using dampers or throttling valves, are not as efficient as a VFD. With a VFD, the fan motor operates at the optimal speed required by the system, resulting in significant energy savings. By reducing the speed of the fan when the demand is low, the VFD ensures that energy is not wasted, leading to reduced electricity consumption and lower operating costs.
Precise motor speed regulation is another advantage provided by fan VFDs. By controlling the frequency and voltage of the AC power supplied to the motor, the VFD allows for fine-tuning of the fan speed. This flexibility is beneficial in applications where varying airflow rates are required, such as in HVAC systems. The VFD enables precise adjustment of the fan speed to match the specific cooling or ventilation needs, providing optimal comfort and efficient operation.
Fan VFDs also play a crucial role in motor protection. They incorporate built-in features such as overload protection, short circuit detection, and thermal protection, which help safeguard the motor against damage due to excessive current, voltage fluctuations, or overheating. This ensures reliable motor operation, prolongs the motor's lifespan, and reduces the risk of unexpected failures.
The applications of fan VFDs are diverse, ranging from commercial and residential HVAC systems to industrial fan installations. They are employed in various settings, including office buildings, manufacturing facilities, data centers, and ventilation systems. In each application, fan VFDs offer precise control, energy efficiency, and motor protection, contributing to improved performance, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced overall system reliability.
In conclusion, fan VFDs are essential devices for controlling and regulating the speed of fan motors. With their ability to achieve energy efficiency, precise motor speed regulation, and motor protection, fan VFDs enhance the performance of HVAC systems and industrial fans, resulting in improved energy savings, optimized airflow, and reliable operation.

Fan Vfd,Abb Variable Frequency Drive,Single Phase Variable Frequency Drive,1 Phase Variable Frequency Drive
WuXi Spread Electrical Co.,LTD , https://www.vfdspread.com