With the continuous development of the power industry, the capacity of generator sets is getting larger and larger, and higher requirements are placed on the performance of generator protection. The theoretical basis of relay protection is based on a clear understanding of the fault law. Further improving the performance of the main protection of large generators requires an in-depth and extensive understanding of the internal faults of the generator. Under the condition of deep understanding of the internal fault of the generator, it is possible to propose and improve the main protection scheme of the generator according to the fault characteristics, and enrich and improve the main protection theory of the generator.
Generator differential protectionAn important characteristic of generator differential protection is that faults or other abnormal signs outside the protection zone must be absolutely stable and reliable, and should not be malfunctioned. The DG2 generator differential protection relay fully meets the above requirements and is well received by users.
The basic DG2 relay can also be equipped with additional printed circuit boards to further expand the functionality. By using a new technique for computing current-type signals, the relay can determine that the current transformer magnetic circuit is saturated due to internal or external faults in the protection zone, thereby determining whether the generator is tripped or maintained in stable operation. This expanded function relay (DG2-Sat) is especially suitable for the protection of important generators or generators with high failure rates in power systems.
In the case of short-circuiting between the stator windings of the generator and its lead-out wires, longitudinal differential protection shall be installed.
According to the wiring method and position, it can be divided into full longitudinal differential and incomplete longitudinal differential. The ratio brake fully differential protection is the primary protection for the internal phase-to-phase short-circuit fault of the generator. The application of differential protection as the primary protection of phase-to-phase short-circuit protection has the longest history. The first thing that people do after digital technology is digital longitudinal protection research. After a differential protection scheme based on instantaneous sampling values ​​is proposed, a scheme for calculating the current phasor of the generator end and the neutral point side using the correlation function method to realize differential protection is proposed, and proportional differential or The differential current squared is the scalar braking criterion for the action quantity, which achieves better selectivity and sensitivity for components with single-sided power supply. In order to eliminate the influence of the load component and further improve the sensitivity, the fault component principle is widely used to improve the traditional differential protection scheme.
Since the traditional differential protection is only effective for the phase-to-phase short circuit between the generator and its leads, the function is narrow. In recent years, an incomplete differential protection scheme has been proposed abroad, and it has been initially applied in large-scale hydraulic turbines. The principle of the differential protection is to connect the neutral point side of the traditional differential protection to the phase-connected branch circuit of each phase, thereby expanding the protection function to phase-to-phase, inter-turn short circuit and branch open welding. A new protection that works. Of course, this function expansion is at the expense of the original single performance compromise, that is, for phase-to-phase or inter-turn short circuits in some parts, the sensitivity of the incomplete differential protection scheme will be lower than that of the differential or lateral difference protection. In addition, the acquisition of incomplete differential neutral current is also difficult, and it also has the problem of TA installation.
The measures to improve the sensitivity factor of differential protection mainly include two aspects:(1) Minimize the unbalanced current. This includes selecting the TA with the same characteristics as possible. For example, select the TA for differential protection of the same model and minimize the burden on the secondary circuit.
(2) Improve the operational characteristics of the differential protection. At present, the differential protection with the line-rate braking characteristic is widely used in the longitudinal unit differential protection of large units, so that the sensitivity coefficient and braking characteristics are effectively improved at the same time.
The protection of the generator stator winding and its lead-out phase-to-phase short-circuit faults have the following main functions:
(1) It has the characteristics of harmonic braking and proportional braking to prevent malfunction of the fault outside the zone, preventing the generator from malfunctioning during overexcitation.
(2) When the current transformer is disconnected, an alarm signal can be issued.
(3) When there is a two-point ground fault on the same phase (out of a zone, outside a little zone), the exit can be operated.
(4) The setting range of the operating current is 0.1 to 1.0 times the rated current.
(5) The operation time (when the current is set twice) is not more than 30ms.
(6) After the differential protection action, the generator protection shutdown 1 action exit relay is used.
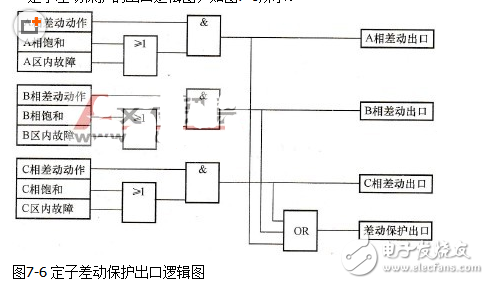
The exit logic diagram of the stator differential protection is shown in Figure 7-6.
The 998 generator differential protection device mainly adopts the 32-bit imported DSP chip and the design principle of “main and rear integrationâ€. It is designed and used for the main protection of various capacity grades and various types of generators. Device.
998 generator differential protection device features:1. This product adopts modular design ideas, high-performance DSP imported chip, hemp ratio differential protection, winding turn-to-turn protection (traverse difference), differential quick-break protection, non-electricity protection, CT disconnection alarm and other protection functions. .
2. The product provides high precision reverse power protection. The internal measuring level current transformer and the protection level current transformer of the device pass the soft switching. The measuring current current transformer sampling channel is adopted under the small current, and the protection level current transformer adopts the channel under the large current, and the multi-level angle compensation is adopted to ensure It ensures high-precision measurement of power in the range of reactive power.
3. The product adopts full metal casing and dual A/D redundant hardware design, which improves the anti-drying ability of the device and improves the measurement accuracy of the device.
4, the product provides a standard RS-485 interface, can also be equipped with other communication interfaces according to user requirements, can be well communicated with the GZP-SCADA microcomputer background monitoring system networking, to achieve remote control.
5. The product is a professional device for generator main protection. It can be used together with 988 generator protection and control device, 989 generator grounding protection device and 988 generator backup protection device produced by our company to form a complete generator. Protection System.
Our solar module has high reliability. Minimized micro-cracks with innovative non-destructive cutting technology. Ensured PID resistance through cell process and module material control.

Bifacial Double Glass Module,Silicon Solar Module,Silicon Mono Solar Module,Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Module
Jiangxi Huayang New Energy Co.,Ltd , https://www.huayangenergy.com