![]() Nowadays, wireless communication is developing rapidly, and the application tentacles are beginning to expand to the connection of various objects and objects. Therefore, even if the 4G network continues to expand, the 5G standard war has long been filled with smoke, especially the narrow-band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) standard, which has become one of the main battlefields for all parties.
Nowadays, wireless communication is developing rapidly, and the application tentacles are beginning to expand to the connection of various objects and objects. Therefore, even if the 4G network continues to expand, the 5G standard war has long been filled with smoke, especially the narrow-band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) standard, which has become one of the main battlefields for all parties.
![]() Nowadays, wireless communication is developing rapidly, and global wireless communication is in full swing. People's demand for mobile communication, audio and video transmission or terminal applications is increasing day by day. The network is everywhere, so even if 4G continues to expand, it will continue to expand. The 5G generation is also coming, and the business opportunities contained in it are even more unlimited.
Nowadays, wireless communication is developing rapidly, and global wireless communication is in full swing. People's demand for mobile communication, audio and video transmission or terminal applications is increasing day by day. The network is everywhere, so even if 4G continues to expand, it will continue to expand. The 5G generation is also coming, and the business opportunities contained in it are even more unlimited.
In China, the Ministry of Economic Affairs expects that the output value of the domestic communication industry will reach 200 billion US dollars after 6 years. Therefore, in order to meet this huge blue ocean of communication, all countries are actively taking the lead in taking the lead and investing a lot of resources and research. The next generation of 5G communication is planned and developed, and it is necessary to master the key technologies and patents to enhance the adoption of the 3rd GeneraTIon Partnership Project (3GPP) standard and help the future of the domestic communication-related industry. development of.
5G communication performance is great
In the case of rapid industrial development, various applications at the user end have also increased. In the face of increasing global demand for data transmission and network capacity, 5G networks have emerged, 3GPP's 5G The relevant standard technologies are expected to be finalized in 2016, and the relevant products will be expected to enter the commercial phase by 2020. In its future development, it will not only require a large transmission rate, but also a number of connections that are several times larger than today. The world will enter the era when everything is connected (Figure 1).
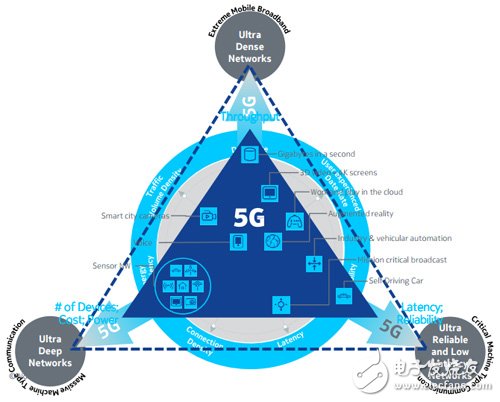
Figure 1 5G development trend
Well-known consulting agency McKinsey pointed out that the application value of the Internet of Things (IoT) will reach 11.1 trillion US dollars in 2025. 5G proposes features such as low latency, high transmission, low energy consumption and large connectivity. 5G mobile communication is expected to have global coverage by 2020. 50 billion terminal products have Internet access, the overall system capacity (Capacity) demand is more than 1000 times more than 4G, and its transmission delay must be less than 1 millisecond (ms), so the performance and technical challenges of the next generation 5G communication will be more than before. More serious.
With the emergence of a large number of application terminals such as smart meters, smart home appliances, smart factories, and wearable devices, more and more work and life need to be solved through smart terminals. For this, high-density links and reductions Terminal cost requirements are getting bigger and bigger, and new technologies are needed to meet such needs.
Analysis of 5G key technologies
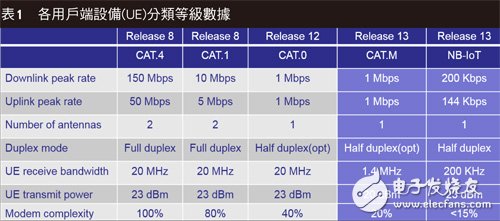
In the future development of 5G, not only the large transmission rate is needed, but also the number of connections that are several times larger than today. The world will enter the era of Internet access. In 3GPP, machine-to-machine (M2M)/machine type communication is first proposed. Machine Type CommunicaTIon, MTC), which is designed with lower equipment costs, lower power consumption, greater coverage, and support for a large number of device connections, but most of them believe that this is only a transitional version. Because its power consumption and construction cost are still too high, it is not enough technology for applications that require lower power consumption and a larger number of connections. Therefore, 3GPP proposes a lower transmission data in R13. Amount, lower equipment cost, and wider coverage technology, called NB-IoT (Narrowband-Internet of Thing), its maximum transmission data volume is 200kbit/s, the bandwidth is also reduced to 200kHz, and its coverage It can be multiplied several times, so all major telecom operators are strongly supportive of this technology (Table 1).
NB-IoT grabs the Internet of Things blue ocean
The Internet of Things has been developed for many years, and various applications and technologies have been proposed. LoRa and SIGFOX also emphasize low power consumption and broad coverage. However, since LoRa and SIGFOX use unlicensed spectrum, they represent anyone. Both of these bands can be used, and many uncontrollable interference problems are formed, which becomes very unreliable in use. Therefore, the world's major telecom operators tend to support the NB-IoT technology proposed by 3GPP due to its use of licensed bands. And NB-IoT can be quickly deployed on Sakamoto's cellular network equipment, saving operators the cost of deployment and quickly integrating long-haul evolution plan (LTE) networks, so it is foreseeable In the future, NB-IoT will be the direction pursued by mainstream telecom operators around the world.
NB-IoT is a low-power wide area wide area (LPWA) technology, which is characterized by extremely low power consumption, wide coverage and a large number of connections. The device coverage can be increased by 20dB. And battery life can be more than 10 years, each NB-IoT carrier can support up to 200,000 connections, and according to capacity needs, you can expand the scale by adding more carriers, so that a single base station can support millions IoT links.
There are several goals in the design of NB-IoT. One is to improve the coverage rate. By reducing the coding rate (Coding Rate), the reliability of the signal can be improved, so that when the signal strength is weak, the signal can be correctly demodulated and improved. The purpose of coverage is to increase the battery life cycle by a maximum of 23dBm, which is about 200mW (mW). In order to reduce the complexity of the terminal, a constant envelope is used for modulation. Constant Envelope) allows the Power Amplifier (PA) to operate in the saturation range, allowing the transmitter to have better efficiency. In the physical layer design, it can also simplify some components and reduce the complexity. In order to reduce the system bandwidth, the bandwidth is designed at 200 kHz, because such a high transmission rate is not required on the Internet of Things, so that it does not need such a large spectrum, and it can be more flexibly allocated in use, and there is an important one. The design goal is to greatly increase the system capacity, so that a large number of terminals can be connected at the same time. One of the methods is to make the subcarrier interval smaller. On the spectrum allocation can be more resilient, cut out more subcarriers are assigned to more terminals.
NB-IoT has a variety of deployment methods in the spectrum. The first one is Standalone. This type of deployment uses the spectrum of independent or Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), which does not interfere with each other. The simplest way to build, but need a spectrum of its own. The second is to use the Guard Band to build. The LTE spectrum edge protection frequency band is used, and the weak signal strength is deployed. The advantage is that it does not need a piece of its own spectrum. The disadvantage is that interference with the LTE system may occur.
The third type is built in the current operating band (In Band), the deployment scenario is shown in Figure 2, and the spectrum used is selected in the low frequency range, such as 700MHz, 800MHz, 900MHz, etc., because in the low frequency band It has wider coverage and better wave-transmission characteristics, and can have a deeper penetration rate for indoor environments.

Figure 2 NB-IoT deployment scenario picture source: NB-IoT enabling new business opportuniTIes, Huawei
However, the current NB-IoT proposed by 3GPP also contains different technologies. Currently, it can be divided into two directions. One is NB supported by Nokia, Ericsson and Intel. - LTE (Narrowband-LTE) and NB-CIoT (Narrowband-Cellular IoT) supported by Huawei and Vodafone. The biggest difference between the two technologies for operators is how much they can be reused in the existing LTE environment. In a networked application.
NB-LTE is almost compatible with current LTE equipment, but NB-CIoT can be said to be a redesigned technology that requires the construction of new chips, but its coverage is expected to increase and equipment costs are even higher. Reduced, so the two technologies can be said to have their own advantages, the following will give an overview of the two technologies.
Adapter Fiber Optic Box,Multimode Fiber Adapter Coupler,All-In-One Fiber Optic Adapter Coupler,Full Complement Fiber Optic Adapter Coupler
Shenzhen Jingtu Cabinet Network Equipment Co., LTD , https://www.jingtucabinet.com