Audio recording has become an essential skill for a variety of purposes, from creating music to producing podcasts and capturing memories. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, filmmaker, or simply someone who wants to document their thoughts and experiences, knowing how to effectively record audio is invaluable. This guide will take you through the fundamentals of audio recording, from understanding the basics to mastering recording techniques and editing processes.

Basics of Audio Recording
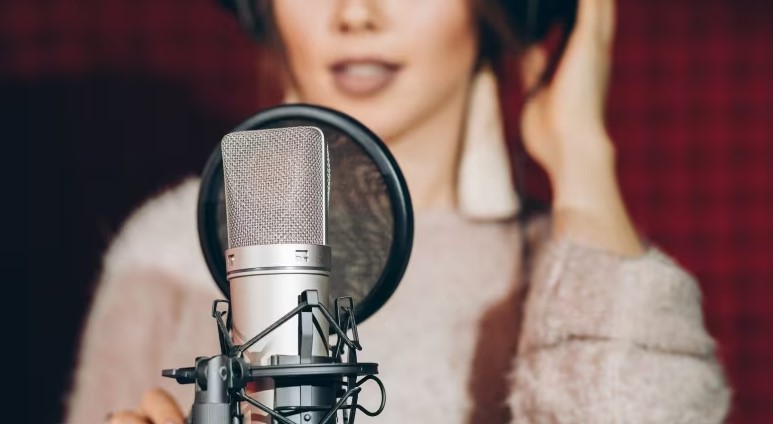
Audio recording is the process of capturing sound waves and converting them into a digital format that can be stored, edited, and played back. It allows for the preservation of performances, conveyance of messages, and expression of creativity.

Importance of Audio Recording
Audio recording serves a multitude of purposes, including music production, podcasting, voiceovers, sound design for film and video, audiobook creation, and more. It enables individuals and professionals alike to preserve performances, convey messages, and express creativity.
Audio Recording Equipment
Audio recording requires specific equipment tailored to the task at hand. Essential components include microphones, audio interfaces, headphones or monitors, and recording software (Digital Audio Workstations or DAWs).

Getting Ready for the Audio Recording Session
Before diving into a recording session, it’s crucial to select an appropriate environment. Look for spaces with minimal background noise and consider acoustic treatment to optimize sound quality.

Investing in high-quality recording equipment is essential for capturing clear and professional-sounding audio. Choose a microphone, like Hollyland Lark M1, that suits your recording needs, select an audio interface compatible with your setup, and ensure you have reliable headphones or monitors for monitoring.

Hollyland Lark M1
Wireless Lavalier Microphone with High-Quality Audio.
Learn MoreSetting Up the Recording Equipment
Proper setup of recording equipment is key to achieving optimal results. Pay attention to microphone placement and angles, and ensure all equipment is correctly connected to your computer or recorder.
Microphones
The heart of any recording setup, microphones come in various types such as condenser, dynamic, and ribbon. Each type has its unique characteristics and best-use scenarios. Choose the right microphone based on your recording environment and the sound you want to capture.
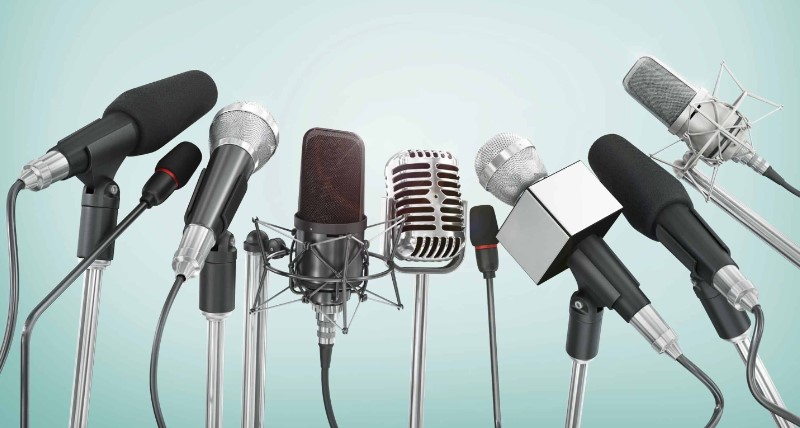

Audio Interfaces
Essential for connecting microphones to your computer, audio interfaces come in different configurations and price ranges. Consider factors like the number of inputs, preamp quality, and connectivity options when choosing an interface.

Recording Softwares
Also known as Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), recording software allows you to capture, edit, and mix audio tracks. Popular options include Pro Tools, Logic Pro, Ableton Live, and Audacity. Experiment with different software to find the one that suits your workflow and preferences. Following are the functions of a digital audio workstation that you should be experimenting with:
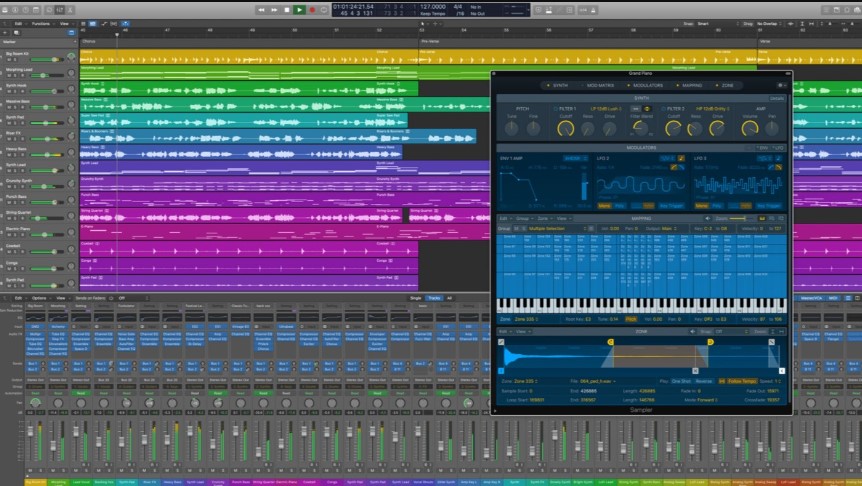
- Levels and Gain Staging: Proper gain staging ensures that your audio signals are neither too quiet nor too loud, preventing distortion and noise. Set appropriate levels on your microphone preamps and audio interface to achieve optimal recording levels.
- Monitoring: Use headphones or studio monitors to monitor your recordings in real-time. This allows you to hear any issues such as clipping, distortion, or background noise and make adjustments on the fly.
- Multi-Microphone Setup: In situations where multiple sound sources need to be captured, such as interviews or musical performances, employ techniques like stereo miking, XY, ORTF, or MS to achieve a balanced and immersive soundstage. Hollyland Lark 150 is the stereo mic that you must have in your recording gear.
Recording Tips and Techniques
Mastering essential techniques and performance strategies can elevate your audio recordings to professional levels.
Microphone Techniques
Microphone placement plays a crucial role in capturing the desired sound. The Proximity Effect, for instance, emphasizes bass frequencies when the microphone is placed closer to the sound source, creating a warmer tone. Experimenting with different distances can help achieve the desired balance between proximity effect and clarity.
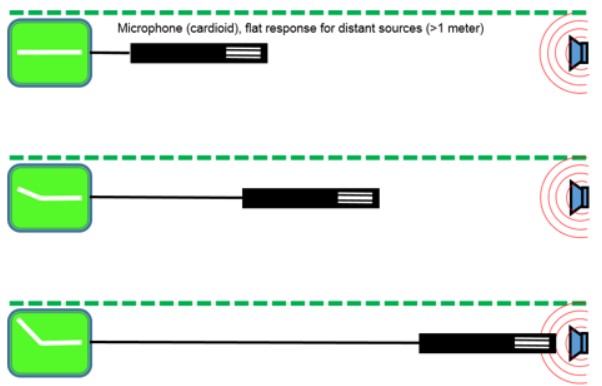
Additionally, understanding the differences between Stereo and Mono Recording is essential. While mono recording captures sound from a single point, stereo recording creates a sense of space and depth by capturing sound from multiple directions. Choose the technique that best suits your project and desired aesthetic.
Performance Tips
Preparing for a recording session involves more than just technical setup. Warming Up your voice or instrument helps ensure a smoother performance by loosening muscles and improving flexibility. Consistency in performance levels is equally important.
Maintain consistent volume and energy throughout the recording to avoid inconsistencies in the final product. Take breaks when needed to rest and recharge, ensuring optimal performance throughout the session.
Monitoring and Listening
Effective monitoring and listening are critical during recording sessions. Using Headphones While Recording allows you to hear yourself or the performers clearly, enabling adjustments in real-time. It also helps prevent sound leakage, ensuring clean recordings. Listening Back to Takes is essential for evaluating performance and identifying any issues or areas for improvement.
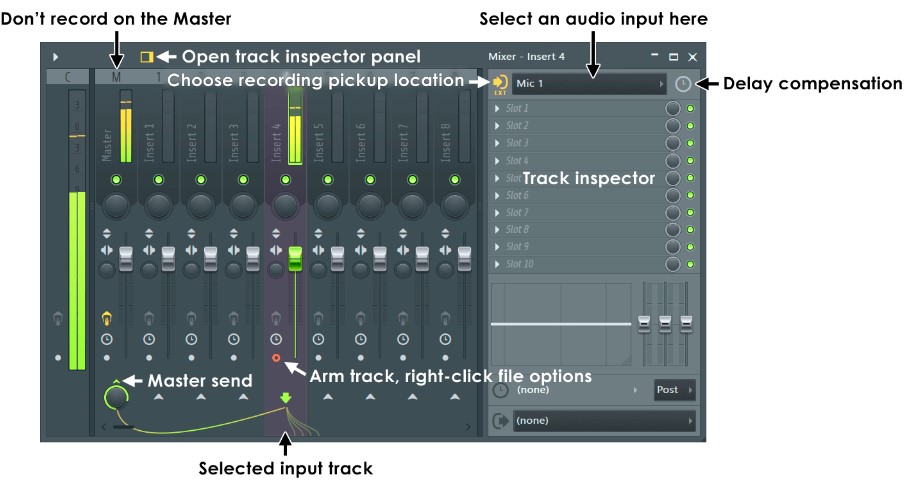
Take advantage of playback features in your recording setup to review takes and make necessary adjustments before finalizing the recording. By incorporating these techniques and tips into your recording process, you can enhance the quality and effectiveness of your audio recordings.
Editing and Processing Post Production
Once you’ve captured your audio recordings, use editing software to trim, cut, and arrange the audio clips as needed. Remove any unwanted noise, pops, clicks, or mistakes to ensure a polished final product.
Basic Editing Techniques
To refine your audio recordings, mastering Basic Editing Techniques is essential. Trimming and Tightening Tracks involves removing unwanted sections and tightening up the timing for a polished result. Comping Takes allows you to select the best parts from multiple recordings to create a seamless composite.
Processing and Effects
Enhance your audio with Processing and Effects to add depth and character. Utilize Equalization to adjust the frequency balance and sculpt the sound. Compression helps control dynamics and adds punch to your tracks. Experiment with Reverb and Other Effects to create ambiance and spatial depth in your recordings.
Mixing
Achieving a balanced and cohesive mix is the goal of Mixing. Balance Levels between different tracks to ensure each element is heard clearly. Use Panning and Stereo Imaging to create width and separation in the mix. Finally, Finalize the Mix by fine-tuning settings and making any necessary adjustments for a professional-sounding result.

Exporting and Sharing Your Recordings
Effectively share and distribute your audio creations to reach your audience and preserve your work for the long term:
Export Formats and Quality
When Exporting your recordings, choose the appropriate format and quality settings to ensure compatibility and fidelity. Consider factors like file size, compatibility with playback devices, and the intended use of the recordings. Common formats include WAV, MP3, and FLAC, each offering a balance between audio quality and file size.
Sharing Platforms and Distribution
Selecting the right Sharing Platforms and Distribution channels is crucial for reaching your audience effectively. Whether you’re sharing music, podcasts, or other audio content, consider platforms like SoundCloud, Spotify, iTunes, and YouTube. Each platform has its audience and features, so choose the ones that align with your goals and target audience.

Archiving and Backup Strategies
Implementing robust Archiving and Backup Strategies ensures the long-term preservation of your recordings. Regularly backup your files to external hard drives, cloud storage services, or dedicated archival systems. Consider redundancy and off-site storage to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, theft, or other unforeseen events. By prioritizing data security and preservation, you can safeguard your recordings for future generations.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of recording audio is a journey filled with exploration, learning, and creativity. By understanding the intricacies of equipment, recording techniques, editing, and distribution, you can unlock your potential to produce high-quality audio content. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to experiment and refine your skills over time. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, the key is to keep pushing boundaries and striving for excellence in every aspect of your audio production journey.
We value your input! Share your thoughts on this guide to recording audio. Did you find the information helpful? Were there any topics you wished were covered in more detail? Your feedback helps us improve and tailor future content to better meet your needs. Leave your comments below and let us know your thoughts!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best microphone for home studio recording?
The best microphone for home studio recording depends on factors like budget and intended use. Popular choices include condenser microphones such as the Hollyland Lark M2, Audio-Technica AT2020 and the Rode NT1-A, and dynamic microphones like the Shure SM58.
Which software is best for recording vocals?Â
Consider Adobe Audition, Pro Tools, GarageBand, Audacity, Riverside.fm, Ableton Live 11, and Audio Director 365.
How can I improve the sound quality of my recordings?
Improve sound quality by focusing on microphone placement, room acoustics, gain staging, and post-processing techniques like EQ and compression.
What are the most common mistakes in audio recording?
Common mistakes include improper microphone placement, poor room acoustics, inconsistent levels, and over-processing during mixing.
How can I improve vocal recordings?Â
Use stereo EQ, mid/side EQ, mid/side compression, Assistive Vocal Balance in Ozone, and Stem Focus for precise control.
How do I reduce echo and reverb in my recordings?
Answer: Reduce echo and reverb by optimizing the recording environment with acoustic treatment and using directional microphones. Apply noise gates, EQ, and reverb reduction plugins during post-production.
How do I set up my recording studio?Â
Start with a computer, a DAW for recording, an audio interface, studio monitors, headphones, a versatile microphone, a MIDI keyboard, and a dedicated workspace.
Galvanized Steel Wire,Stay Wire,Guy Wire,Earth Wire
HENAN QIFAN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. , https://www.hnqifancable.com