The oil pressure regulator has two functions:
â‘ Adjust the oil pressure of the oil supply system to keep the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the injector constant. â‘¡Buffer the oil pressure fluctuation caused by the fuel injection of the fuel injector and the oil pump.
The structure of the fuel oil pressure regulator:
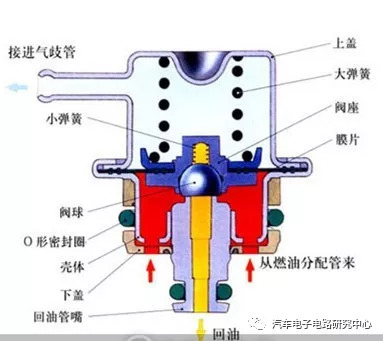
1. Composed of diaphragm, oil return valve, spring, oil return pipe and aluminum alloy shell. 2. The valve body is fixed on the metal diaphragm. A ball valve is installed between the valve body and the valve. The ball valve is supported by the shrapnel. The small spring between the ball valve and the valve body keeps the ball valve in contact with the valve. 3. There are 3 joints on the shell, which are respectively connected with the oil inlet pipe, the oil return pipe and the vacuum pipe between the throttle valve and the intake manifold.
The working principle of oil pressure regulator:
Spring chamber and lower fuel chamber. And the opening of the overflow valve is controlled by the diaphragm to keep the pressure balance of the upper and lower chambers.
2) When the fuel pressure in the fuel chamber rises above the combined force of the spring pressure and the vacuum gas pressure, the diaphragm buckles upwards, the regulator valve opens, and part of the fuel flows from the ball valve to the fuel tank through the return port, reducing the fuel pressure. When the pressure drops to the control oil pressure set by the regulator, the ball valve is closed to maintain a certain pressure in the oil path from the one-way valve of the oil pump to the pressure regulator.
Fuel pressure regulator inspection
1. The failure of the fuel pressure regulator and its effect:
The main failure of the fuel pressure regulator is that the diaphragm ruptures and the spring tension becomes weaker after fatigue attenuation. When a failure occurs, it will directly affect the accuracy and supply of the fuel injection pressure difference, resulting in unstable engine fuel supply, difficult starting, weak acceleration, unstable idling, increased fuel consumption, and black smoke.
2. Testing method â‘ Oil pressure testing:
Connect the oil pressure gauge to the fuel line to measure the idling fuel pressure. When the vacuum hose on the regulator is removed, the system pressure should increase by about 50kPa. Otherwise, it indicates that the fuel pressure regulator is faulty and should be replaced. â‘¡Working inspection: Use a wire to bridge the two inspection holes of the fuel pump, turn on the ignition switch, and let the fuel pump run for 5 minutes and observe the oil pressure. This oil pressure is the fuel pressure regulator's holding oil pressure. If the pressure drops, it indicates that the fuel pressure regulator is leaking and should be replaced.
The output characteristics of the oil pressure regulator:
1) When the gas pressure in the intake manifold drops (vacuum increases), the diaphragm moves upwards, the opening of the oil return valve increases, and the amount of oil return increases, and the oil pressure in the fuel distribution pipe decreases to maintain and change the intake air. The pressure difference of the manifold is constant (0.25MPa).
2) When the gas pressure in the intake manifold increases (vacuum decreases), the diaphragm moves down, the opening of the oil return valve decreases, the oil return decreases, and the oil pressure in the fuel distribution pipe increases, maintaining and changing The pressure difference of the intake manifold is constant (0.25MPa).
3) The output characteristics of the oil pressure regulator reflect the relationship between the oil pressure in the fuel distribution pipe and the pressure of the intake manifold. The function of the oil pressure regulator is to ensure that the fuel injection volume of the injector is not affected by the negative pressure of the intake manifold and fuel supply. The influence of system oil pressure is only determined by the opening time of the injector valve.
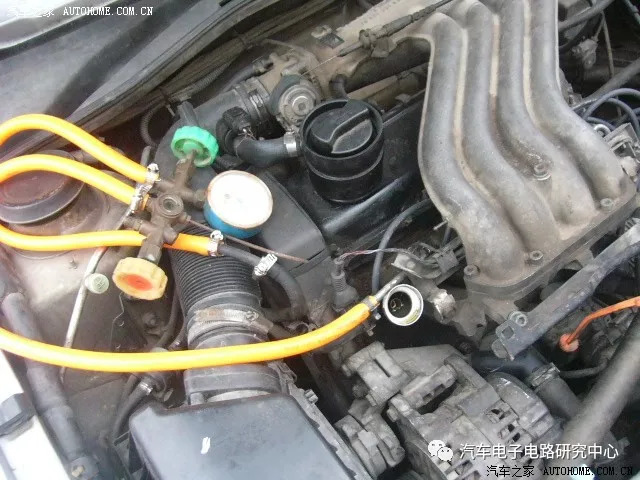

Fuel system pressure detection method
1. Pressure relief:
First unplug the fuel pump fuse, relay or fuel pump plug, and then start the engine until the engine turns off by itself, restart the engine 2 to 3 times, and then remove the negative electrode of the battery.
2. Install fuel pressure gauge:
Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the fuel inlet pipe in series. Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the pressure gauge on the vehicle with a pressure measuring port. When removing the fuel pipe, use a towel or cotton cloth to pad under the fuel pipe interface to prevent fuel from leaking on the ground.
As shown in the figure below, install the fuel pressure gauge to the fuel pressure gauge adapter. The pressure gauge is generally installed at the oil outlet of the gasoline filter or the oil inlet of the fuel distribution pipe. The fuel pressure gauge can be connected to the pressure gauge on vehicles with pressure measuring ports.
â‘ Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and check whether the fuel leaks.
â‘¡ Start the engine and check if the fuel leaks.
â‘¢ Read the reading on the fuel pressure gauge. The idling speed is generally 0.25MPa or meets the technical regulations of the vehicle type.
â‘£When checking the working pressure at idle speed, the oil pressure should rise to 0.3MPa when the vacuum tube is unplugged. Otherwise, the oil pressure regulator should be replaced.
⑤Turn off the engine and check the change of the fuel pressure gauge reading. The pressure gauge reading should remain unchanged within 5 minutes.
3. Detection of oil pressure: static oil pressure, idling oil pressure, maximum oil pressure, remaining oil pressure
Static oil pressure:
Without starting the engine, use a jumper wire to connect the two terminals on the oil pump diagnostic connector ("+B" and "FB" terminals of Toyota models), and turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position to make the oil pump work and static oil pressure Generally around 300 KPa.
Idle speed oil pressure:
Install the fuel pump fuse or relay, start the engine, and make the fuel pump run at idling speed. At this time, the oil pressure gauge reads the idling working oil pressure. The normal value of Toyota vehicles should be 200~300KPa.
Maximum oil pressure:
Clamp the oil return pipe with pliers covered with a soft cloth. At this time, the oil pressure gauge reads the maximum oil supply pressure of the oil pump, which is generally 2 to 3 times the normal working oil pressure.
Remaining oil pressure:
Loosen the fuel pipe clamp, the engine is turned off, and the fuel pump stops running for 10 minutes, the pressure of the fuel pipe should be greater than 150 KPa.
Pay attention to unit conversion: 1Mpa=1000Kpa; 1bar=1kgcm2=14.2psi=100Kpa
Oil pressure analysis
The oil pressure gauge reading oil pressure is zero, oil pressure is normal, oil pressure is too high and oil pressure is too low.
If the oil pressure is zero
First check the fuel tank storage, and whether the oil passage is severely leaked, and whether the fuel filter is completely blocked. After eliminating the possibility, the oil pressure is still zero. You need to check the control circuit of the fuel system, such as whether the fuse is blown, whether the relay is not working, whether the wiring harness of the fuel pump circuit is open, whether the fuel pump is damaged, etc.
If the oil pressure is too high
Mainly check whether the vacuum tube on the top of the pressure regulator is loose or ruptured and leaks, or whether the oil return pipe of the oil pressure regulator is blocked.
When the fuel pressure is too low
Or the oil pressure drops rapidly within 2-5 minutes after the fuel pump stops working. Under the premise of eliminating the leakage of the oil circuit, there will be leakage in the fuel injector, fuel pressure regulator failure, fuel filter blockage, and fuel pump failure.
Switch Junction Box,Electrical Wall Box,Waterproof Outlet Box,Electrical Adapter Box
FOSHAN SHUNDE LANGLI HARDWARE ELECTRICAL CO.LTD , https://www.langliplastic.com