Like the motor used, a three-phase asynchronous motor consists of a stator (stationary part) and a rotor (rotating). Each contains electrical windings that carry current, creating a magnetic field that interacts to create torque that spins the rotor and load. This particular machine is a "totally enclosed, fan-cooled" motor, or TEFC for short. This means that the motor is hermetically sealed so no air is exchanged between the inside and the outside of the motor, the internal air is stirred by paddles at the end of the rotor body, and the fan blades are located outside the motor housing and pull the air through the motor housing, thereby Help cool the motor.
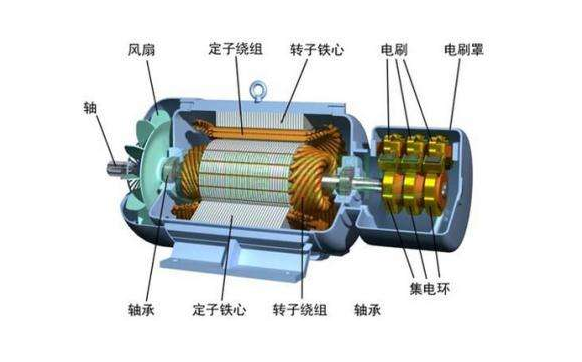
Three-phase asynchronous motor stator, which belongs to the fixed part of the motor, is mainly composed of stator iron core, stator winding, frame and so on. The function is to generate a rotating magnetic field and fix the entire motor.
stator core
It is made of mutually insulated silicon steel sheets stacked into a cylindrical shape, and there are evenly distributed grooves on the inner circumference surface for placing three-phase windings. The role is part of the magnetic circuit of the motor and on which the stator windings are placed. The stator core is generally punched and laminated by 0.35~0.5mm thick silicon steel sheets with insulating layers on the surface, and evenly distributed slots are punched in the inner circle of the core to embed the stator windings.
The stator core slot types are as follows:
1. Semi-closed slot: The efficiency and power factor of the motor are high, but it is difficult to wire and insulate the windings. Generally used in small low-voltage motors.
2. Semi-open slot: can be embedded with formed windings, generally used for large and medium-sized low-voltage motors. The so-called formed winding means that the winding can be insulated in advance and then put into the slot.
3. Open slot: It is used for inserting and placing forming windings, and the insulation method is convenient. It is mainly used in high-voltage motors.
stator winding
The stator winding is formed by connecting many coils. The coils are wound from copper or aluminum conductors with insulation. Its function is the circuit part of the motor, which is fed with three-phase alternating current to generate a rotating magnetic field. The stator winding is connected by three windings with the same structure, which are separated by 120° electrical angle from each other and arranged in teams.
The main insulation items of the stator winding are as follows: (guarantee the reliable insulation between the conductive parts of the winding and the iron core and the reliable insulation between the winding itself).
1. Insulation to ground: the insulation between the stator winding as a whole and the stator core.
2. Interphase insulation: insulation between stator windings of each phase.
3. Turn-to-turn insulation: insulation between turns of each phase stator winding.
Machine base
The frame is used to install the stator iron core and the fixed end cover, and supports the rotor through the two end covers. Fix the entire motor with sufficient strength.
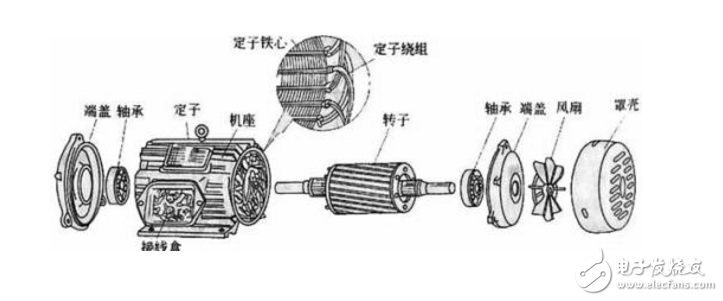
The rotor is the running part of the motor, which is composed of an iron core, a rotor winding and a rotating shaft.
rotor core
The rotor core is composed of many silicon steel sheets with small grooves on the outer circumference. The small grooves are used to place the rotor windings.
rotor winding
The rotor winding is embedded in the small slot of the rotor iron core, and the rotor winding can be divided into a cage rotor winding and a wire wound rotor winding. The cage rotor winding is to put metal bars in the small slots of the rotor iron core, and then use guide rings to connect the bars at both ends of the iron core, so that any bar and its corresponding bar are guided at both ends. The ring constitutes a closed winding, which is called a cage rotor winding because it resembles a cage. There are two types of cage rotor windings: copper bar rotor windings and cast aluminum rotor windings, as shown in Figure 8. The copper bar rotor winding is to put copper bars in the small slots of the rotor core, and then weld them together with metal end rings at both ends; while the cast aluminum rotor winding is to cast aluminum on the core by casting. Guide bars, end rings and vanes.
The structure of the wire wound rotor winding is to embed the windings wound with insulated wires in the rotor core according to certain rules, and then connect the windings according to the delta or star connection method, most of which are connected in the star shape. After the windings are connected, 3 phase wires are drawn out, which are connected to the 3 copper collector rings (also known as slip rings) of the rotating shaft through the inner hole of the rotating shaft. The brushes are in frictional contact, and the brushes are connected to the varistor through wires, so that the current generated by the rotor winding forms a loop through the collector ring, the brushes, and the varistor. Adjusting the varistor can change the resistance of the rotor winding circuit, thereby changing the current of the winding, thereby adjusting the speed of the rotor.
shaft
The shaft is nested in the middle of the rotor core. When the stator winding is connected to three-phase alternating current, a rotating magnetic field will be generated, and the rotor winding will rotate under the action of the rotating magnetic field. It drives the rotating shaft to rotate through the rotor iron core, and transmits the power from the rotating shaft.
Automotive Staple,Automotive Industrial Staple,Moistureproof Automotive Staple,Hog Ring Blunt Galvanized Nail
Zhejiang Best Nail Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.beststaple.com